Hello lovely Ribbot Army <3
I have decided to start a weekly (possibly biweekly) thing where I will be sharing different medical conditions to raise awareness for them. I will also be providing further reading at the end if anyone wants to continue with their own research. If anyone has any they would like me to do feel free to DM me them <3
This week I am beginning with hypermobility spectrum disorders (used to be known as joint hypermobility syndrome).
HSD also known as hypermobility spectrum disorders are connective tissue disorders that cause joint hypermobility, instability, injury, and pain. GI issues, fatigue, headaches, and autonomic dysfunction are also commonly seen symptoms.
While most babies and children are born flexible, only around 20% keep their hypermobility into adulthood. For most people hypermobility is not an issue. For many dancers and gymnasts hypermobility is seen as an advantage. Hypermobility that is painless is referred to as asymptomatic joint hypermobility.
Problems occur when the joints not only are hypermobile but also unstable. The instability comes from the connective tissues not being able to hold the joint in place properly leading to a heightened chance of sprains, dislocations, and other injuries.
HSD is considered to be a spectrum disorder meaning no two people show symptoms the exact same way. For example some people with HSD may have a history of constant subluxations/dislocations but little to none GI issues while someone else may have severe headaches but mild joint instability. These two people both have HSD even though they present entirely differently.
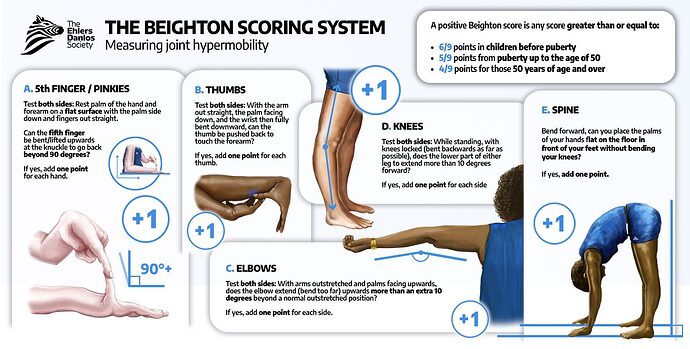
The Beighton scale is one of the ways to screen for HSD.
While it is a helpful tool for screening for generalized joint hypermobility, it is unhelpful with diagnosing three of the four types of HSD.
The four types of HSD are:
Generalized HSD (G-HSD): HSD in which joint hypermobility occurs throughout the body
Peripheral HSD (P-HSD): HSD in which joint hypermobility is limited to the hands and feet
Localized HSD (L-HSD): HSD in which joint hypermobility occurs in a single joint or group of joints in the same area
Historical HSD (H-HSD): HSD in which there is history of generalized joint hypermobility, but without current evidence of generalized joint hypermobility on exam
(bullet points taken from What is HSD? - The Ehlers Danlos Society)
HSD is treated many different ways through many different specialists. To help with the joint instability most people with HSD will see a PT to strengthen muscles.
HSD is diagnosed through a physical examination and medical history. Doctors must confirm that the joint hypermobility is in fact causing issues and is not just asymptomatic. These problems include, subluxations/dislocations, joint pain and loss of function, joint damage, such as cartilage tear, early joint degeneration, soft tissue damage and injury, chronic pain, and/or poor proprioception.
Further reading!
-What is HSD? - The Ehlers Danlos Society
-Joint Hypermobility Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatments
-Joint hypermobility syndrome - NHS